Mediterranean Garden Society

Mediterranean Garden Society

Toxic and allergenic plants in mediterranean gardens
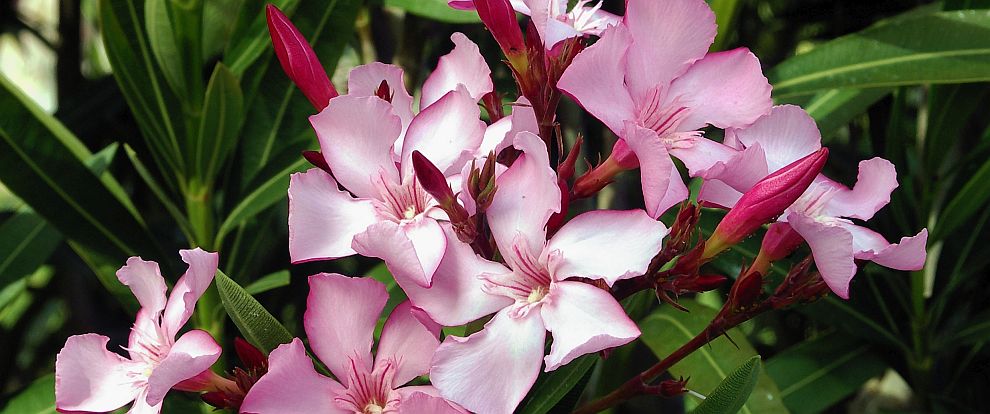
The photograph at the top of this page shows Nerium oleander, all parts of which are very poisonous (Photo Wiki Commons)
The plants listed here can cause:
Poisoning if parts are eaten or smoke is inhaled when the plant is burned.
Phytodermatitis if contact with the skin has occurred.
Acute contact dermatitis, either allergic or toxic : Acute allergic contact dermatitis occurs only after previous sensitization. The power of contact allergens varies greatly. In the case of Primula obconica it takes only 4 days. Acute toxic reaction occurs in areas where the skin has been directly exposed to the noxious agent (euphorbia, poison ivy).
Chronic contact eczema, either toxic or allergic.
Chronic toxic reaction after repeated exposure to the noxious agent.
Phototoxic reaction after contact in the presence of light or sun (Ruta, Citrus, Ficus, Hypericum, Plumbago and others).
Mechanical irritation on account of irritating parts of plants (Opuntia, Lagunaria, Ampelodesmos, Miscanthus sinensis).
Ceratostigma plumbaginoides
Plumbaginacea
China
Causes contact dermatitis with vesicles. It is advisable to wear gloves when pruning the plant.
Cestrum nocturnum
Solanaceae
South America
The fruits are more poisonous than the leaves. Inhaled smoke from burned plants is poisonous.
Daphne gnidium
Thymelaceae
Mediterranean
A pretty plant from the Mediterranean macchie. All parts, especially the seeds, are very poisonous.
Datura stramonium
Solanaceae
Europe, Asia, Africa
Contains hyoscyamine.
All parts, particularly roots and seeds are extremely poisonous. The plant has hallucinogenic properties. Used in religious rituals. "Asthma cigarettes" are smoked. Sometimes soya grist can contain seeds of datura. Death in horses and cattle after feeding with soya grist containing 0.3% seeds has been rep4orted from veterinary clinics. Use in cosmetics is prohibited.
Datura suaveolens
= Brugmansia suaveolens Solanaceae
Brazil
Indians use it in religious and magic rites. Even the scent can have a narcotic effect.
Attention: when pruning this datura, disturbances of vision (mydriasis) may occur.
Euonymus europaeus
Celastraceae
Europe
Contains evonosid. All parts, especially the fruits, are poisonous. In adults, 35 fruits cause death after 12-18 hours.
Attention: twigs are poisonous to animals too, prevent dogs from playing with them.
Euphorbia characias
Euphorbiaceae
Mediterranean
Acute contact allergen. Sap in contact with the eyes can cause blindness. Pollen may cause respiratory allergy (asthma).
Euphorbia marginata
Euphorbiaceae
North America
Contains ingenol. Common name: "Snow-of-the-Mountain". Acute toxic reaction. Causes skin irritation and inflammation of the skin.
Ficus carica
Fig-Tree, Moraceae
Mediterranean
Contains furocumarin. The sap causes photocontact dermatitis. Unripe fruits are poisonous. Avoid damaged fruits, pressed dry fruits and fruit paste because mycotoxins may develop, causing liver damage and cancer.
Lagunaria patersonii
Malvaceae
South Pacific
Tree with fruits. Open fruits shed stiff very irritating fibres which cause itching and inflammation of the skin for weeks.
Fruits should be removed if the tree is close to a swimming pool.
Lantana camara
Verbenaceae
West Indies, tropical South America
All parts are poisonous. Cultivation is prohibited in S. America. Leaves are used in ethnomedicine. Of the genus Lantana, L.camara is the most poisonous species.
Skin contact: photo-toxic reaction.
Nerium oleander
Apocynaceae
Mediterranean
Contains 28 glycosides. All parts are very poisonous, as is honey from the pollen. Deaths have been reported from the USA where the wood was used for barbecue sticks!
Used as rat poison. Drinking tea of dried leaves can cause death after 2-3 hours.
The smoke is very toxic when inhaled. After pruning do not burn the waste!
Nicotiana glauca
Solanaceae
South America
An invader to the Mediterranean.
All parts are highly toxic if eaten. In Mexico the dried leaves were smoked like tobacco, although they do not contain nicotine.
Ornithogalum longibracteatum
South Africa
Easily mistaken for Urginea maritima. The difference is that Ornithogalum has green skins covering the bulb, while Urginea has red skins covering the bulb, which is much bigger. The bulb is poisonous but the leaves contain sap which is able to heal burn blisters. The bulb is medically used in preparations for treating heart diseases.
Phytolacca americana
Phytolaccaceae
North America
Contains saponin glycosides and phytolaccatoxin.
All parts are very poisonous, especially the roots and seeds. 10 berries are lethal for children. Yet the use of plant for colouring wine and sweets is reported from ancient times. In Mallorca, the plant is sometimes found growing next to a church.
Plumbago capensis
Plumbaginaceae;
South Africa
Contact-dermatitis. All members of the Plumbaginaceae contain plumbagin.
Primula obconica
Primulaceae
China
Contains primin, a highly potent contact allergen. P. obconica is sold in great quantities in garden centres. The primin responsible for allergic reaction was analysed by Paul Karrer, Zurich, Nobel prize winner in chemistry. Research to eliminate primin from this beautiful primula is now in progress.
Ricinus communis
Euphorbiaceae
India, Tropical Africa
Contains ricin, the most toxic of all proteins. 5-6 seeds for children and 10-20 seeds for adults are fatal. The pretty seeds are used for making necklaces! Residue from the oil-pressing process is used in fertilizers. 20 gr are lethal for cattle, 0.2 gr/kg for horses and 1-2 gr/kg for other domestic animals.
The Ricinus antigen has a very high potency. When inhaled, for instance in fertilizing lawns, the dust can cause severe respiratory allergies. The oil of Ricinus seeds is listed as a prohibited item.
Solandra maxima
Solanaceae,
Mexico, Venezuela
Climber. The flower gives off a fine fragrance but causes irritation to the eyes if contact is too close.
Solanum jasminoides, Solanum rantonnetii
Solanaceae
Tropical South America
The fruits are very poisonous, including those of the blue variety.
Thevetia peruviana
Apocynaceae
Mexico, South America
Contains glycosides and thevetin. All parts are very poisonous. 8 to 10 seeds are deadly for adults.
Urginea maritima
Liliaceae
Mediterranean
All parts are very poisonous, particularly the bulb. 1.5 gr of pulverized bulb are lethal for adults. Children have died eating 1½ teaspoons of syrup. Preparations are used as rat poison. Beware when shredding as cut pieces of the plant cause severe dermatitis. Use in cosmetics is prohibited. Urginea can be easily mistaken for Ornithogalum.
Wisteria sinensis
Fabaceae
China
Contains glycosides. The bark and roots are poisonous.
Seeds are extremely poisonous, also for dogs. 2-5 seeds are lethal for children.
THE MEDITERRANEAN GARDEN is the registered trademark of The Mediterranean Garden Society in the European Union, Australia, and the United States of America